Contents
JRC Tech Seminar Vol.6
Hello everyone, do you like our last blog about the introduction to MIMO? In part 2, we will describe how MIMO works in detail, hope you will like it!
MIMO
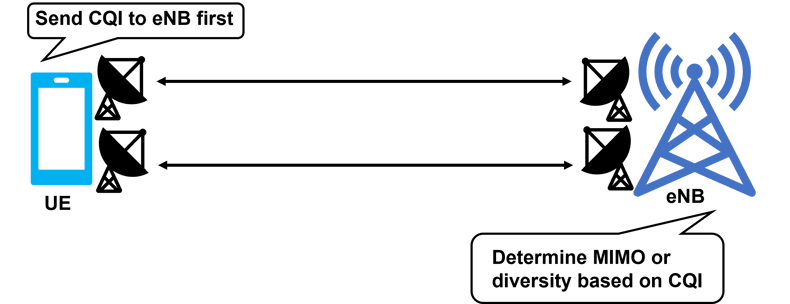
MIMO has the same antenna configuration as spatial diversity, but its purpose is different: it is created to improve speed rather than to counteract fading. Therefore, the reception status (=CQI*1) is transmitted in advance by the UE side to the eNodeB, and it determines whether to use MIMO or Diversity.
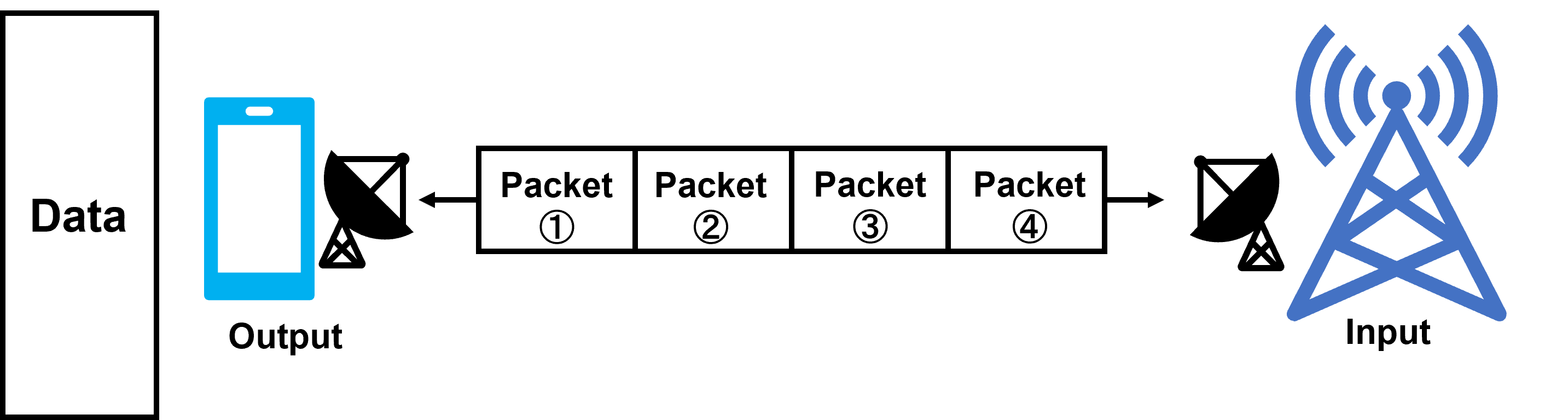
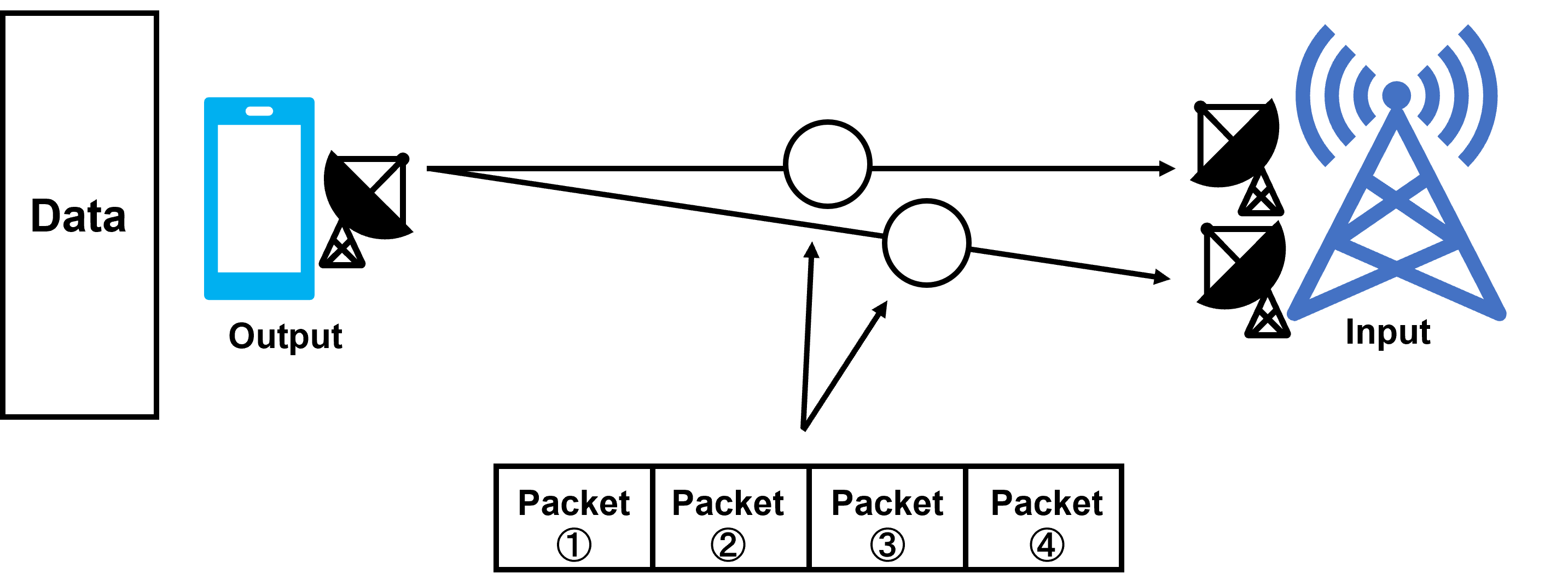
In diversity, the same data is sent to each antenna and the one with the higher reception level is selected to achieve stability, but in MIMO, different data is sent to each antenna to double the communication speed by the number of antennas. In LTE, there are 2*2MIMO and 4*4MIMO.
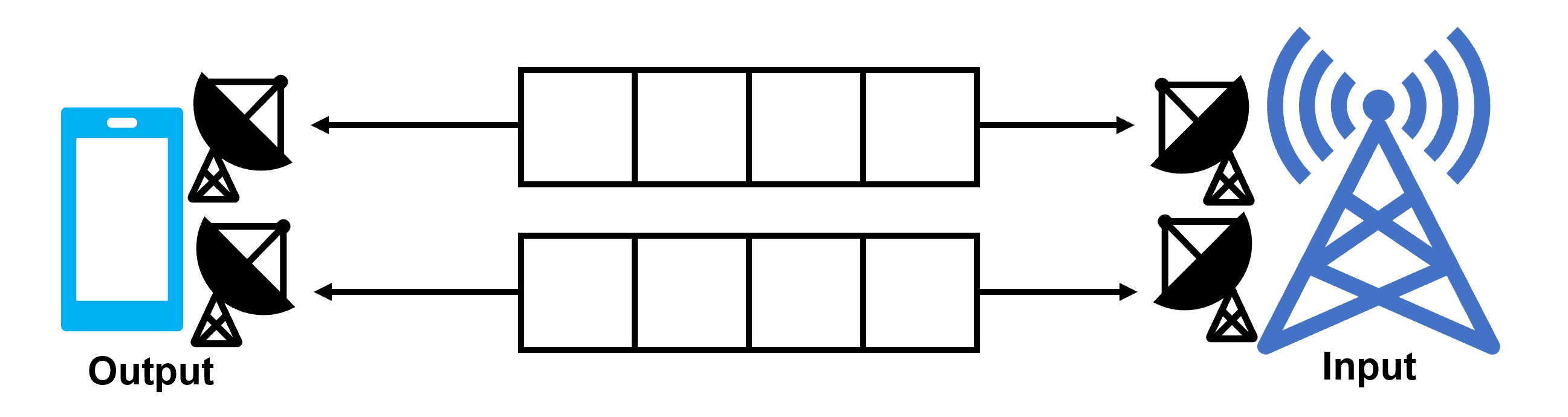
Receiving a higher level of reception makes the data more reliable
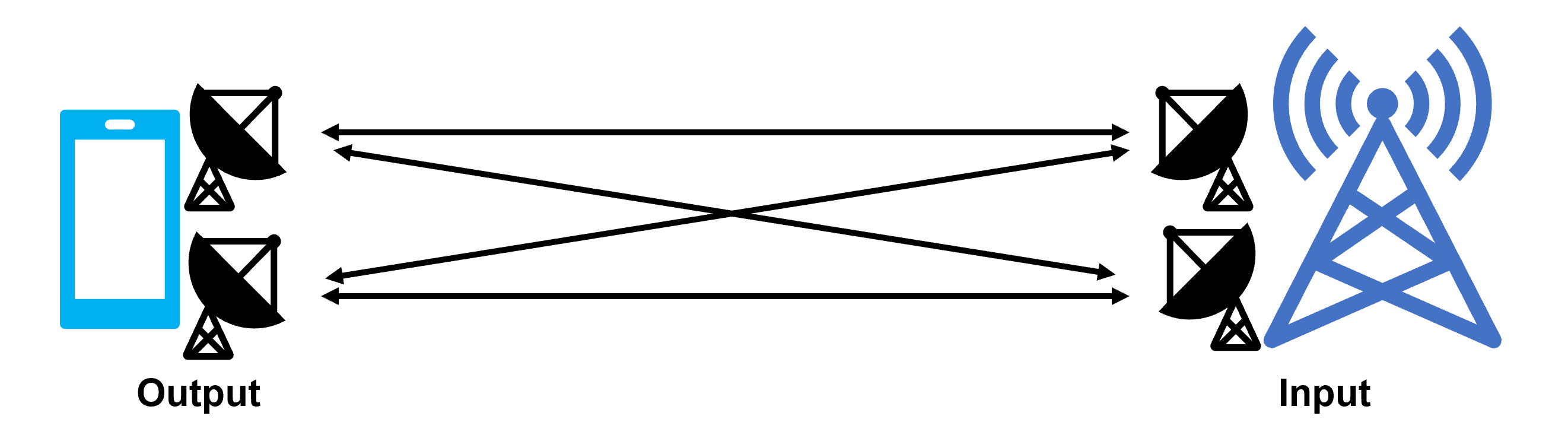
Doubling of speed by sending data simultaneously with multiple antennas
*1 Based on Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), Signal-to-Interference-plus-Noise ratio (SINR), and Signal-to-Noise and Distortion Ratio (SNDR), the UE determines the CQI and transmits to the eNodeB. The modulation method and transport block size are determined based on the CQI.
Demodulation
In the case of MIMO, a characteristic value is determined for a combination of antennas before communication in order to demodulate data sent from multiple transmitting antennas to each receiving antenna. This value is determined as the number of transmitting antennas x the number of the receiving antenna matrices.
⇒ y: received data, h: channel information matrix, x: transmitted data.
For 2*2MIMO, it would be as follows
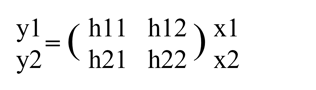
By multiplying the columns of this composite signal (y1 or y2) by the inverse matrix obtained from the matrix of characteristic values, it is possible to extract the signal emitted by each transmitting antenna.
Summary
Compared to single-antenna communication, multi-antenna communication can provide more reliable data transmission and higher transmission speeds.
Multi-antenna transmission provides higher data reliability due to fading countermeasures, and MIMO can further increase data transmission speed by MIMO enables data communication between multiple antennas, so the communication speed can be n times faster than that of SISO*2.
*2 Only when communication stability is high (high CQI, low channel correlation, etc.). When it is low, take a spatial diversity approach, sending and receiving the same data with multiple antennas and receiving the one with the lower loss.
| Type |
Data Reliability |
Throughput | Image |
| SISO |
△ |
△ |
Send (receive) packets on a single route |
| MISO | 〇 | △ |
|
| SIMO | 〇 | △ | 
Send the same data over different paths and receive the one with less loss |
|
Multi-antenna to multi-antenna (Diversity) |
〇 | △ |  Send the same packets over multiple routes and receive the one with less loss |
| MIMO | △ | 〇 | 
Sending (receiving) packets over multiple routes |
For further information about Private LTE, please check out our other blogs and use cases. If you have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact us.